|
Group Risk Management System
To consolidate its role as a corporate group that truly serves the community of which it is a member, the Kiyo Financial Group (Kiyo Holdings, Inc. and companies under its umbrella, hereinafter the “Group”) ensures operational soundness and higher profitability through risk and profit management frameworks that enable it to provide high value-added services.
Financial markets continue to evolve amid deregulation and the development of new financial techniques and information technologies, creating still more opportunities for financial institutions to generate profit. At the same time, risks directly faced by such institutions — including credit, market, liquidity, operational, systemic, legal, and settlement risk — are increasing both in scope and diversity.
Against this backdrop, the Group recognizes that risk management is one of its most important management tasks and works to improve its risk management systems.
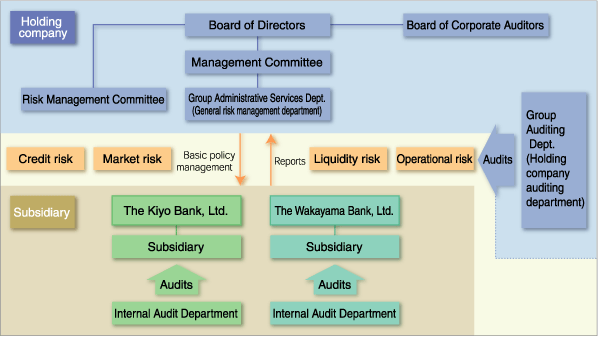
Specifically, we have established a Risk Management Committee under the direct control of the Board of Directors and the Group Management Division to coordinate risk management across the Group. We have also compiled a Basic Policy for Risk Management and Risk Management Regulations, laying down the basic items for risk management, as well as a General Risk Management Rule to enable overall and quantitative assessment of diverse kinds of risk. In this way, we are building a comprehensive risk management system for the entire Group.
We have also set up risk management committees and departments to coordinate the management of individual risk categories in both of the core entities of the Group, Kiyo Bank and Wakayama Bank. We operate risk management systems in each entity corresponding to the type and scale of risk.
The Group will continue upgrading its risk management capabilities to ensure sounder management operations and more stable profits.
Credit Risk Management
The Group defines credit risk as the possibility of incurring losses due to the inability to recover loan principal or interest from a borrower as a result of the deterioration of the borrower’s business situation.
As a framework for managing credit risk, we have compiled a set of “credit risk management” rules to serve as a basic policy and framework for credit risk management. To ensure adequate controls over credit risk, we are taking a range of steps, including the establishment of a set of guidelines for credit ratings and an integrated credit risk control system.
Kiyo Bank and Wakayama Bank continue to upgrade credit risk management — separating credit screening functions from the business promotion sections. It operates as a discrete screening system through the implementation of rigorous self-assessment, verification of the accuracy of self-assessments through the Corporate Auditing Office and so on, to protect the soundness of our assets in line with the above basic policy and regulations. A further measure to protect asset soundness is the establishment of a department to support borrowers in their efforts to improve their business performance.
Market Risk Management
The Group defines market risk as the possibility of incurring losses due to fluctuations in the value of bank assets due to various market-related factors such as changes in securities prices, interest rates and foreign-exchange rates.
We have compiled a set of Market Risk Management Rules and employ Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Basis Point Value (BPV) techniques to accurately measure market risk. The Group is also putting in place appropriate risk control systems, such as maximum allowable risk limits and loss-cutting functions, that prevent excessive risk-taking.
Against this backdrop, Kiyo Bank and Wakayama Bank (the banking subsidiaries of Kiyo Holdings, Inc., hereafter the “Banks”) are working to ensure stable earnings by discussing ways of achieving an appropriate balance between risk and return in the Risk Management Committee and the ALM Strategic Committee.
The Group has a risk management framework incorporating a system of mutual checks and balances in which the front office executes market-related transactions, the middle office controls risk and the back office handles administrative processing and account settlements.
Liquidity Risk Management
The Group defines liquidity risk as the possibility of incurring losses due to the inability to secure required funds, leading to restrictions on the flow of funds, and the inability to avoid interest rates that great exceed market rates.
Because the greatest liquidity risk faced by the Group is a funding crisis caused by a run on deposits, the Banks work to allay customer concerns in transactions by ensuring stable earnings and a robust financial position. At the same time, the Group maintains maximum vigilance in regard to the early detection of signs of abnormality in funding and strictly manages its funding position.
We have compiled our “Liquidity Risk Management Rules” and classified the status of fund flows into four categories: “normal,” “requiring attention,” “causing concern,” and “critical.” We are building a framework enabling appropriate responses to each category.
Operational Risk Management
The Group defines operational risk as the possibility of posting losses due to the inappropriate operation of internal processes resulting from human or computer error, the malfunctioning of computer systems or the suffering of damage as a result of a natural disaster such as an earthquake or fire.
In other words their is a wide range of risk categories outside of credit, market and liquidity risk, such as administrative risk, system risk, and reputational risk.
Administrative Risk Management
Administrative risk refers to the possibility of posting losses due to the failure to perform duties appropriately or as a result of an accidental event or similar cause.
The Banks have established rules and procedures for managing administrative risk and aim to consolidate customer trust through more accurate and rigorous administrative processing. Regular training and guidance given at branches are used to enhance administrative performance at the branch level.
To avert business risk and preempt the occurrence of problems, the auditing office carries out audits at branches and offers guidance on the accurate, error-free performance of duties and the prevention of mishaps.
System Risk Management
System risk refers to the possibility of incurring losses due to computer system-related problems, such as unexpected system stoppages and operational errors, as well as improper use of computer systems and leakage of information.
To preempt such risks, the Banks take rigorous measures during the development of system projects to optimize process and quality management. Additionally, online circuits are duplicated and firewalls have been installed to prevent unauthorized third-party access to systems. We have taken security and other measures to prevent information leakage.
We have also compiled a manual for crisis response and have taken a variety of measures enabling us to minimize the impact should a failure of any kind occur.
The Group will continue to strengthen its system risk measures to provide safer services for its customers.
Reputational Risk Management
The Group defines reputational risk as the possibility of incurring losses due to the spreading of rumors and other false information that could affect the Company’s reputation in markets and among customers.
To prevent the materialization of such risks, we proactively disclose information in a timely and appropriate way, while constantly increasing the transparency of our operations.
|

